If you have been in the cryptocurrency arena for some time, you’ve probably heard the terms “mainnet”, “testnet”, and “devnet” thrown around on every project. Simply put, these are the technical terms used in crypto to denote the major development stages of any blockchain product. Each stage offers vital upgrades and features that help in enhancing the DApps, smart contracts, DeFi projects, NFTs, or anything else you build on the blockchain.
The mainnet, short for the main network, is always the “active, live, and publicly available” version of the blockchain project – the final product. Blockchain testnets (test network) and devnets (development network) provide proxy environments that developers could practice with/ experiment with their projects before releasing the “real thing”. This allows them to build their DApps without the costs, risks, and pressure accumulated if they were building on the mainnet.
By removing these risks, developers get the freedom to innovate and build their decentralized applications (DApps), act as validators, issue new tokens, or test new smart contracts. Additionally, testnets allow them to test the robustness and bug-free nature of the mainnet without actually interfering with the mainnet.
It has almost become an unsaid rule that developers must launch a testnet and/or devnet during a test period before launching their mainnet platform. For example, quantum-resistant blockchain, QAN Platform, plans to launch a testnet version later this quarter to test the first-of-its-kind DApps.
The worlds apart: Testnets vs Mainnet
As alluded to, blockchain mainnets are the live, public, and primary protocols that allow real transactions to occur by utilizing the platform’s real native cryptocurrency. These transactions are then verified and recorded on the distributed ledger. Testnets and devnets offer the experimentation environment of mainnets, to users and developers, respectively.
So, as an inspiring crypto head, how can you tell the difference between them?
The easiest way to tell them apart is most testnets and devnets will be labeled accordingly. For example, Ethereum’s testnets – Ropsten, Rinkeby, and Kovan – are clearly labeled “Test Networks” on Metamask with the mainnet labeled “Ethereum Mainnet”.
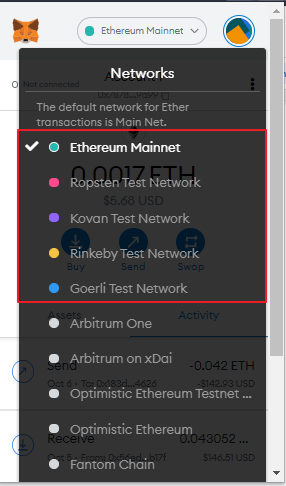
The network identifier (ID) for mainnet and testnets also differ. Whenever a developer, or node, wants to join the chain, they need to choose a network ID to join. For instance, Ethereum’s Mainnet network has an ID of 1 while the Ropsten, Rinkeby, and Kovan Testnet have a chain ID of 3,4, and 42 respectively.
On the transactions front, mainnets offer real and valuable transactions stored on the actual blockchain while testnet/devnet only allow pseudo transactions with no real value. Moreover, cryptocurrencies or tokens on the devnet/testnet have no monetary value while mainnet coins possess real value and can be exchanged. Testnets and devnet also do not charge any transaction fees while on the mainnet, every transaction is paid for using the native coins of the blockchain. Finally, miners on the mainnet have an economic incentive to earn real coins once they validate transactions while testnets and devnets offer no real economic benefit.
Moving from testnet to mainnet in action
To get a feel of how mainnet and testnets work in action, let’s have a look at the QAN blockchain platform. It is important to note that a mainnet and a testnet are two separate networks that operate independently from each other.
QAN leads the development of quantum-resistant blockchains offering high throughput, easy integration, and low latency to the users. The blockchain is quantum-resistant via its use of lattice-based algorithms to offer post-quantum cryptography.
Later this quarter, the QAN blockchain platform will launch its inaugural testnet version to allow developers and builders to create and test their DApps on the QAN blockchain. This allows developers to build any type of quantum-resistant DApp on QAN including smart contracts, DeFi solutions, tokens/cryptocurrencies, and non-fungible tokens, popular as NFTs.
Via their testnet version, developers can experiment with the functionalities of their DApps to check how they will perform once launched on the mainnet. QAN testnet allows developers to save on using valuable QAN tokens when testing their projects before they go live to the public. Once tested and satisfied that the DApps work, they are then deployed to the mainnet where they will go live and be available for anyone to use.
🔥@QANplatform achieves record 5-minute⏱️rapid cloud deployment — 80% faster than industry leaders.
Works with @awscloud @Azure @googlecloud @digitalocean @linodehttps://t.co/xZjr5NcrKt#QANplatform $QANX— QANplatform (@QANplatform) September 28, 2021
Unlike other testnet versions, QAN offers developers an easy-to-setup environment. Via Docker (a deployment app), developers get all the packages and libraries needed for setting up their QAN private blockchain in minutes. Developers can then “define later which of the data will be published on the QAN public blockchain”, once the mainnet is launched.
Users can deploy their tenets in minutes on Google Cloud, Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, Digital Ocean, or Linode.
Testnets wild importance to the blockchain ecosystem
While the mainnet is the final and only valuable chain across the blockchain versions, testnets and devnets also have their own advantages, majorly, offering an experimentation environment to enhance the platform.
The experimentation environment ensures constant development on the platform. In order to improve and innovate in the blockchain industry, constant rigorous tests on smart contract functionalities, transactions, and minting/mining processes have to be carried out. Having testnets enhance the developmental spirit across the industry by providing a simulation on how the actual mainnet will work, once launched.
As the saying goes, humans are prone to errors hence the need to have preventive measures when developing blockchains. Testnets are useful in preventing bugs on the main network since they can be easily detected and solved without losing users’ money or crashing the system. This ensures the transparency, security, and integrity of the system are maintained.
In short, blockchain testnets are a key component of the blockchain ecosystem that offers simple and risk-free avenues for testing and debugging developers’ code. Testnet and devnet networks provide significant value to the blockchain mainnets they serve whether it is in writing smart contracts, building DApps in NFTs, or creating DeFi protocols.
Recommended for You
- BitOasis Fundraising Season Secured $30 Million
- Has Bitcoin Catched The Upward Track Crossing $50K Again ?
- Under 30 Seconds Inflation Hedging Coin (IHC) Raised $10 Million
- Nimbus and Nethermind Run Merge Event To Prepare for PoS Transition
- Dogecoin (DOGE) on a Slow-Growth as Rival Shiba Inu (SHIB) Dominates








