- Polygon proposes replacing MATIC, with POL as the universal token across all its networks.
- Polygon 2.0 upgrade aims to enhance security, scalability, and sustainability.
- POL will serve as a unified token for all Polygon-based networks, including PoS, zkEVM, and Supernets.
Polygon, a leading Ethereum scaling solution, has put forth a groundbreaking proposal to replace its existing native token, MATIC, with POL as the universal token across all Polygon networks as part of its highly anticipated Polygon 2.0 upgrade.
Polygon 2.0 aims to bolster the security, scalability, and sustainability of the Polygon ecosystem. Also, POL would serve as a unified token for all Polygon-based networks, including Proof of Stake (PoS), zkEVM, and Supernets. It represents a significant advancement as the third generation of native assets—a hyperproductive token with groundbreaking features.
1/ Today, the next technical proposal of Polygon 2.0 is unveiled:
— Polygon (Labs) (@0xPolygonLabs) July 13, 2023
POL, the upgraded token of the Polygon protocol! 💫
POL is the next generation native token, designed to secure, align and grow the Polygon ecosystem.
Watch the video to get an idea how cool it is, then 🧵 pic.twitter.com/Gn7KcHpWEY
With the adoption of POL, MATIC token holders will experience a seamless transition, as their tokens will be upgraded to POL on a 1:1 ratio. This upgrade will eliminate the existence of two separate native tokens, streamlining the ecosystem and aligning the community.
Further, POL offers several key advantages. Holders of POL will have the opportunity to participate as validators across multiple chains, enabling them to validate and secure various Polygon networks.
In addition to the ability to validate multiple chains, POL introduces the concept of multiple roles for validators. Validators can engage in activities such as zero-knowledge proof generation, participation in Data Availability Committees (DACs), and other valuable tasks within its ecosystem.
Polygon 2.0: The Four-Layered Structure
To enhance security and scalability while ensuring atomic and instantaneous transactions, Polygon 2.0 introduces a four-layered structure.
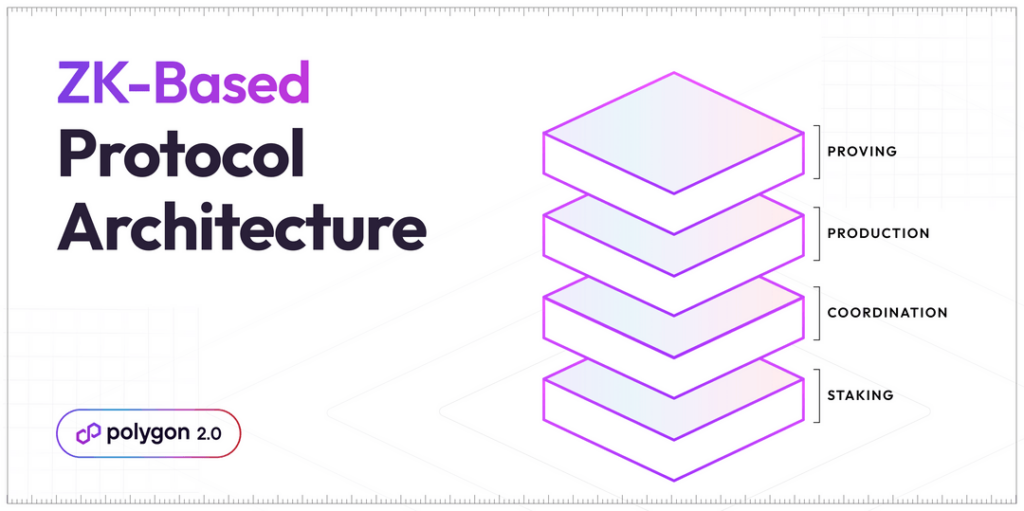
The first layer, known as the Staking Layer: maintains the existing validator manager contract on the Ethereum blockchain. The second layer, called the Interoperability Layer, builds upon the Staking Layer and connects all Polygon chains using bridges.
The third layer, known as the Execution Layer. That enables Polygon chains to process blocks in a similar manner to Ethereum blocks. It comprises various components such as peer-to-peer (P2P) communication, consensus mechanisms. Finally, the Proving Layer, the fourth layer in the architecture, is responsible for generating proofs for both internal and cross-chain transactions within each Polygon chain.
Recommended for you







